me
280 words
1 minutes
CMOS-compatible high aspect ratio silicon-on-glass in-plane micro-accelerometer
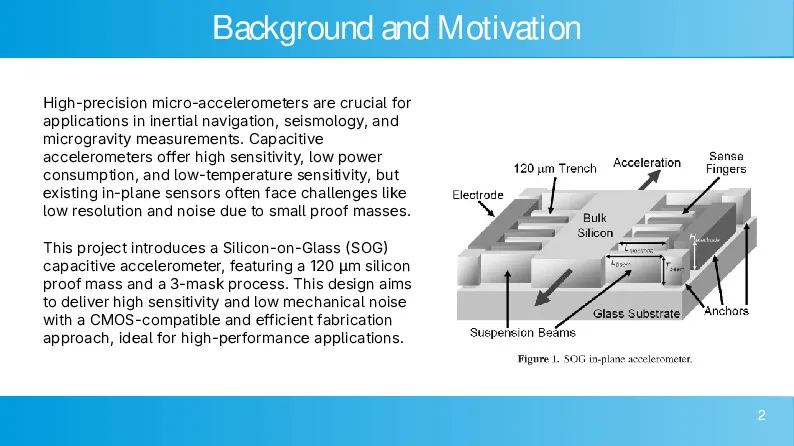
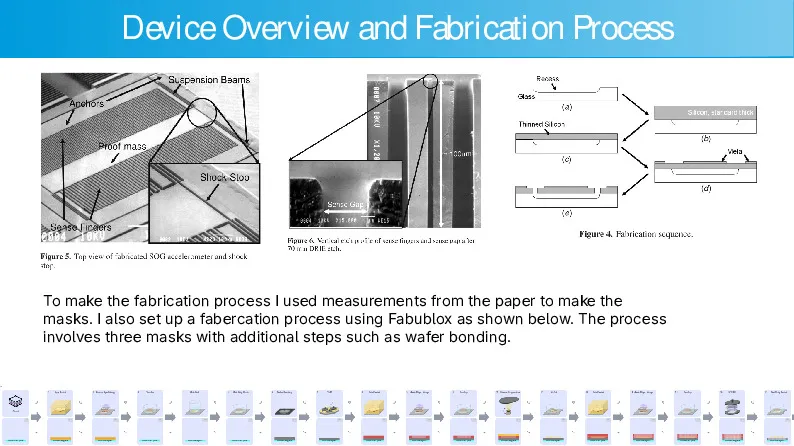
This is the culmination of a semester’s work doing nanofabrication, and I decided to make my project on building a micro accelerometer. The majority of the design work was done in Python using the gdspy library and managed by my own Gitea instance. I have included the slides summarizing the results of my project and the steps needed to fabricate the sensor.
In short, the accelerometer works, and the results are measured by the table below relating capacitance change to acceleration. I also included the first part of the code used to generate part of the design. 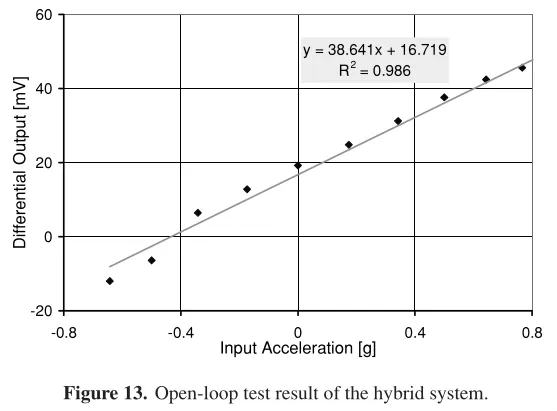
import gdspy
SIZ = 200
# Create a new GDS library
lib = gdspy.GdsLibrary()
# --- Step 1: Create a New Cell for Accelerometer Layout ---
cell = gdspy.Cell("SOG_Accelerometer")
# Define the layers for each mask
base_glass_layer = 1 # Layer 1 for glass etching (for recess)
glass_etch_mask = 2
silicon_layer = (
3 # Layer 2 for silicon structures (proof mass, suspension beams, sense fingers)
)
metal = 4 # Layer 3 for metal contacts (Cr/Au)
# --- Step 2: Glass Etching Layer (First Layer) ---
# Recess in the glass substrate (for the silicon wafer to be bonded)
# Assuming a simple rectangular recess in the glass
base_glass_layer = [
gdspy.Rectangle((0, 0), (200, 200), layer=base_glass_layer),
]
glass_etch_mask = [
# side beams
gdspy.Rectangle((2, 40), (18, 160), layer=glass_etch_mask),
gdspy.Rectangle((182, 40), (198, 160), layer=glass_etch_mask),
# corners things
gdspy.Rectangle((2, 2), (18, 18), layer=glass_etch_mask),
gdspy.Rectangle((2, SIZ - 2), (18, SIZ - 18), layer=glass_etch_mask),
gdspy.Rectangle((SIZ - 2, 2), (SIZ - 18, 18), layer=glass_etch_mask),
gdspy.Rectangle((SIZ - 2, SIZ - 2), (SIZ - 18, SIZ - 18), layer=glass_etch_mask),
]

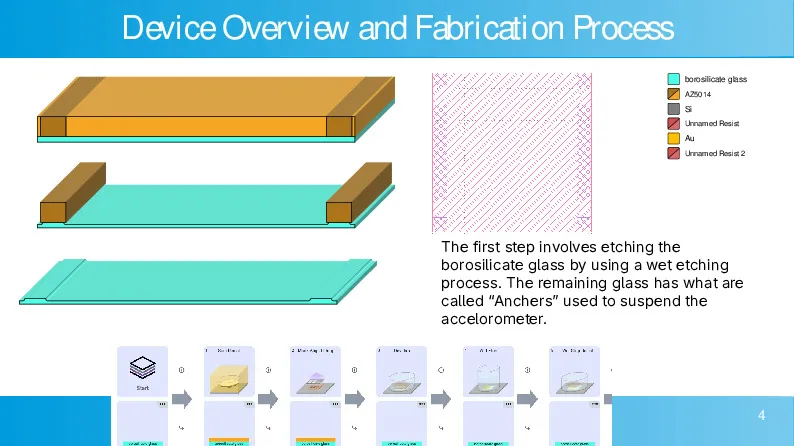
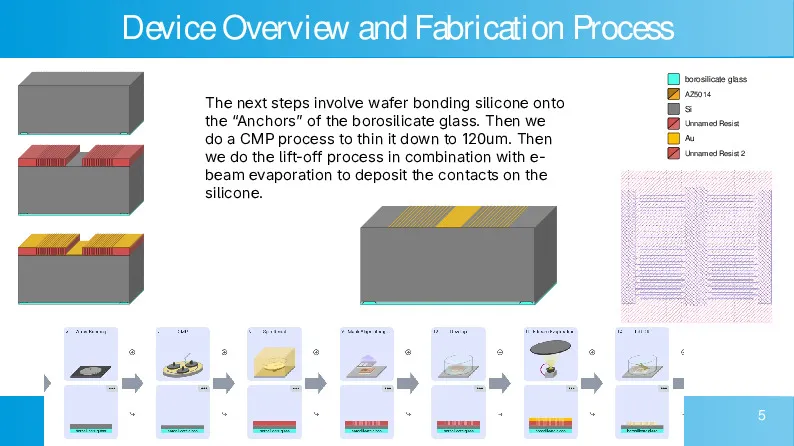
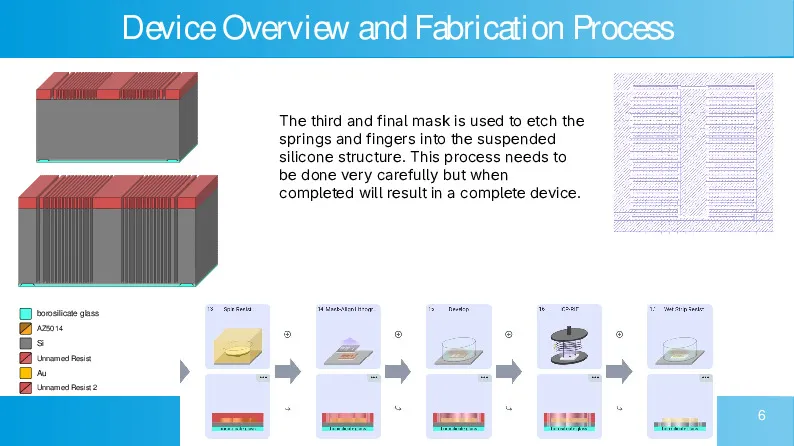
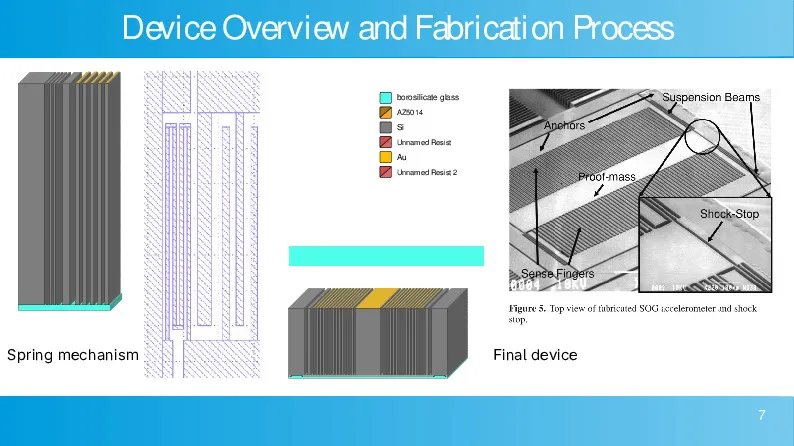
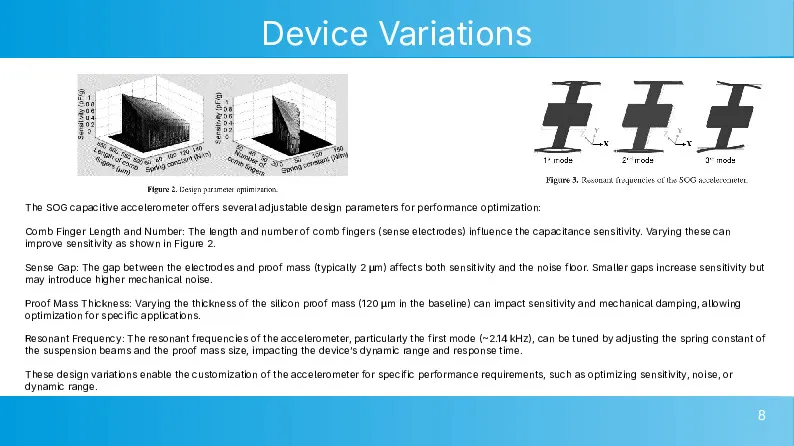
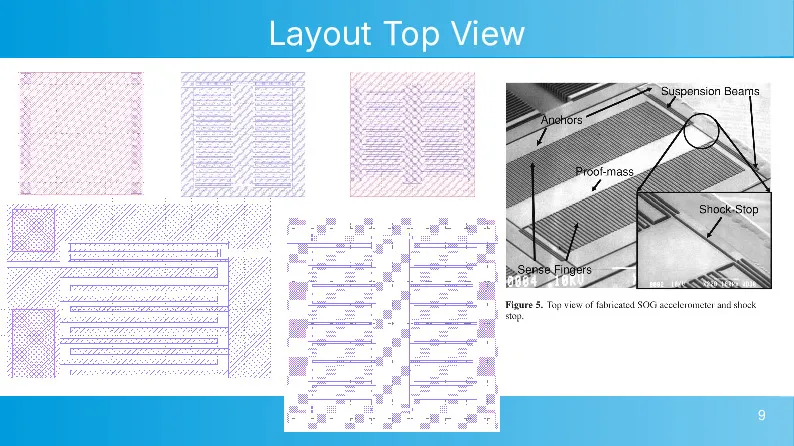
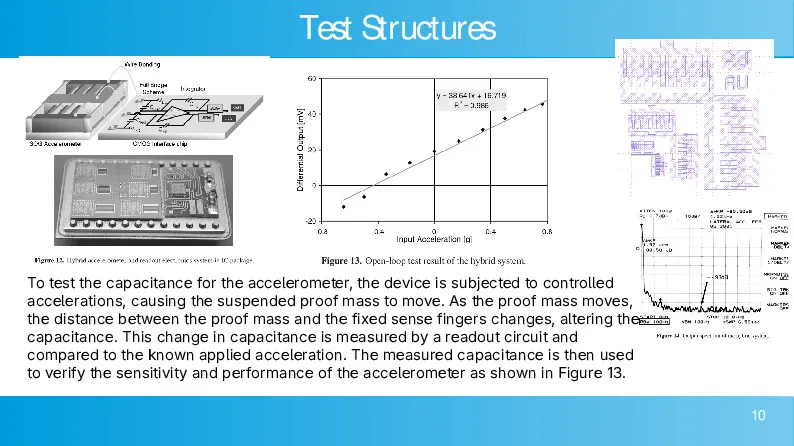
CMOS-compatible high aspect ratio silicon-on-glass in-plane micro-accelerometer
https://andrewhartley.tech/posts/nanofab-final-project/
